We are committed to providing one-stop service for steel pipe products to customers around the world.

We are committed to providing one-stop service for steel pipe products to customers around the world.
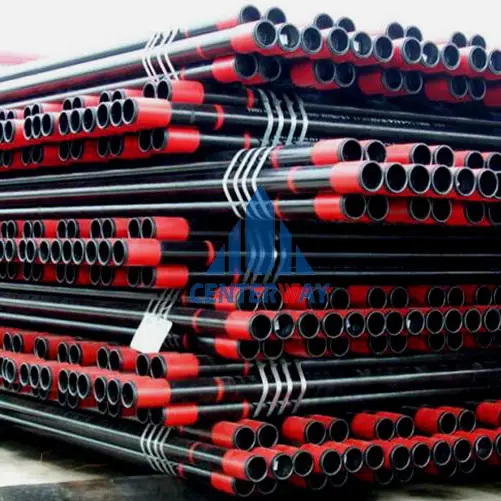
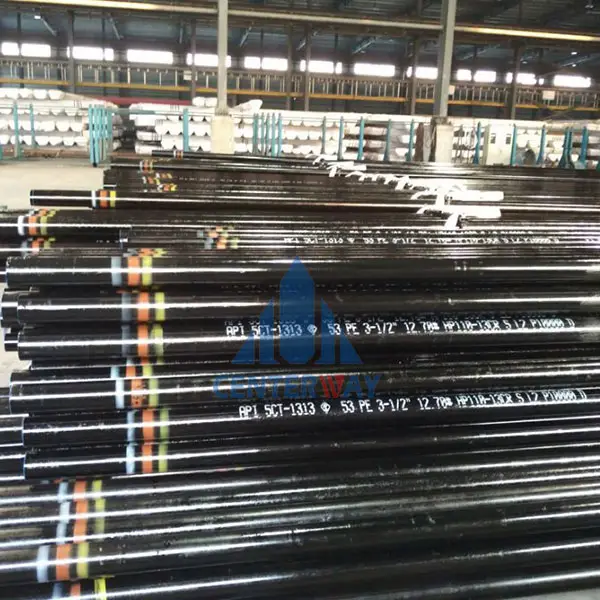











Tubing is a relatively small-diameter pipe that is run into a well to serve as a conduit for the passage of oil and gas to the field surface facilities for processing. Tubing must be adequately strong to resist loads and deformations associated with production and workovers. Further, tubing must be sized to support the expected rates of production of oil and gas.
Sizes and Materials
Tubing pipes are manufactured in seamless and welded execution, in the size range of 1.050 to 5 1/2 inches (consult this article to see the AP5CT tubing pipes sizes) and in the following material grades: H-40, J-55, K-55, N-80, L-80, C-90, T-95, P-110, Q-125
End Connections
The main types of connections for tubing pipes are NUE (non-upset), EUE (external upset) and premium. Corrosion resistance under sour service conditions is a very important OCTG characteristic, especially for casing and tubing.
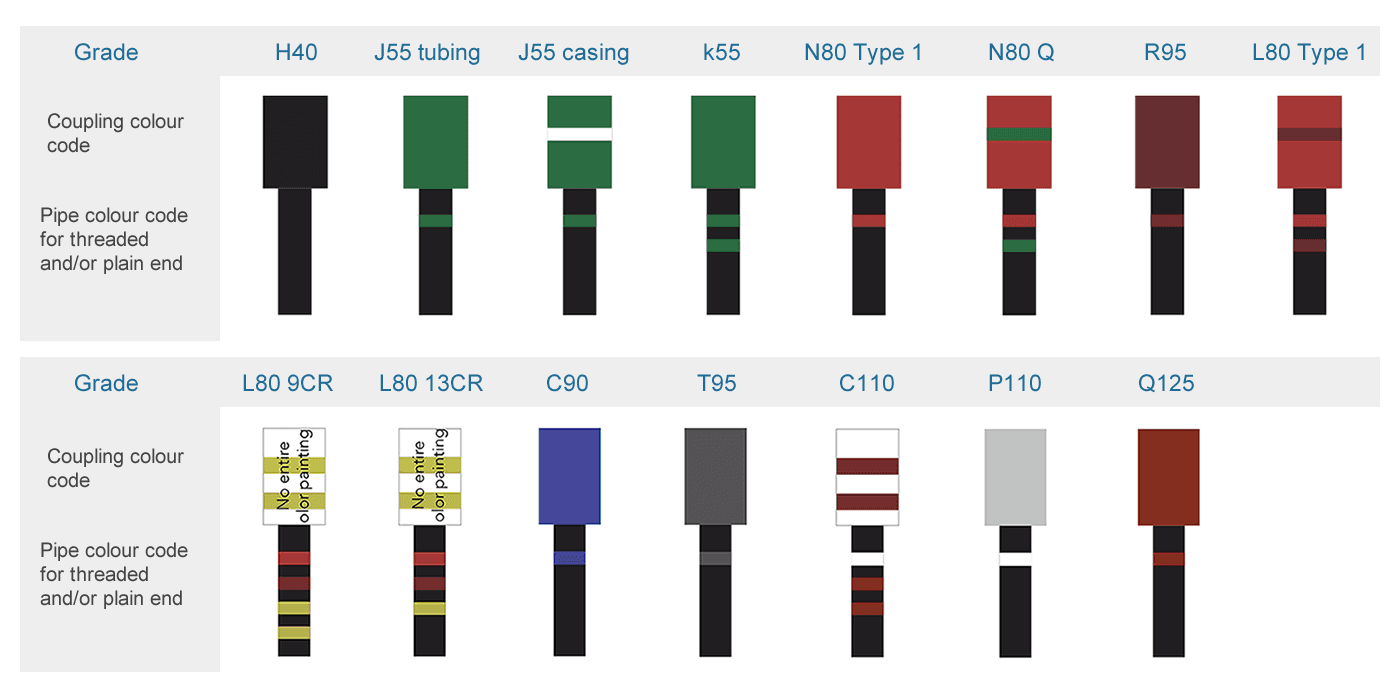
More casing pipes and their colors
|
Oil Tubing |
Range 1 |
Range 2 |
Range 3 |
|
6.10~7.32 |
8.53~9.75 |
11.58~12.80 |
Label
D Outside diameter mm
Wall thickness mm
C type of end-finish
1
2
NU T&C
EU T&C
IJ
H40
J55
L80
N80
C90
T95
P110
1.9
2.75
2.9
4
48.26
3.68
PNUI
PNUI
PNUI
PNUI
PNUI
PNUI
3.65
3.73
2.76
48.26
5.08
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
4.42
-
-
48.26
6.35
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
2 3/8
4
-
-
60.32
4.24
PU
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
-
4.6
4.7
-
60.32
4.83
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
5.8
5.95
-
60.32
6.45
-
-
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
6.6
-
-
60.32
7.49
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
7.35
7.45
-
60.32
8.53
-
-
PU
-
PU
PU
-
2 7/8
6.4
6.5
-
73.02
5.51
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
7.8
7.9
-
73.02
7.01
-
-
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
8.6
8.7
-
73.02
7.82
-
-
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
9.35
9.45
-
73.02
8.64
-
-
PU
-
PU
PU
-
10.5
-
-
73.02
9.96
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
3 1/2
7.7
-
-
88.9
5.49
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
-
9.2
9.3
-
88.9
6.45
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
10.2
-
-
88.9
7.34
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
-
12.7
12.95
-
88.9
9.52
-
-
PNU
-
PNU
PNU
PNU
14.3
-
-
88.9
10.92
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
15.5
-
-
88.9
12.09
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
4
9.5
-
-
101.6
5.74
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
PN
-
10.7
11
-
101.6
6.65
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
PU
-
13.2
-
-
101.6
8.38
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
16.1
-
-
101.6
10.54
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
4 1/2
12.6
12.75
-
114.3
6.88
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
PNU
-
15.2
-
-
114.3
8.56
-
-
P
-
P
P
-
Note: P—plain-end;N—non-upset, with threaded and coupled;U—external-upset, with threaded and coupled;I—whole joint
|
Pipe Types |
Pipe Size (mm) |
Tolerances |
|
|
Hot Rolled |
OD |
≤159 |
±1.0% |
|
>159 |
±1.20% |
||
|
WT |
≤20 |
±12.5% |
|
|
>20 |
±10.0% |
||
|
Cold Drawn |
OD |
≤30 |
±0.20mm |
|
30-50 |
±0.30mm |
||
|
>50 |
±0.8% |
||
|
WT |
≤3 |
+12% -10% |
|
|
>3 |
±10% |
||
API Spec 5CT – Specification 5CT/ISO 11960, Specification for Casing and Tubing, Eighth Edition, Petroleum and natural gas industries-Steel pipes for use as casing or tubing for wells
Mechanical Properties:
|
Group |
Grade |
Type |
Total elongation under load % |
Yield Strength M pa |
Tensile strength min Mpa |
Hardness |
||
|
min |
max |
HRC |
HBW |
|||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
|
2 |
J55 |
- |
0.5 |
379 |
552 |
517 |
- |
- |
|
K55 |
- |
0.5 |
379 |
552 |
655 |
- |
- |
|
|
N80 |
1 |
0.5 |
552 |
758 |
689 |
- |
- |
|
|
N80 |
Q |
0.5 |
552 |
758 |
689 |
- |
- |
|
|
3 |
L80 |
1 |
0.5 |
552 |
655 |
655 |
23 |
241 |
|
L80 |
9Cr |
0.5 |
552 |
655 |
655 |
23 |
241 |
|
|
L80 |
13Cr |
0.5 |
552 |
655 |
655 |
23 |
241 |
|
|
C90 |
|
0.5 |
621 |
689 |
689 |
25.4 |
255 |
|
|
C95 |
- |
0.5 |
655 |
724 |
724 |
- |
- |
|
|
T95 |
|
0.5 |
655 |
724 |
724 |
25.4 |
255 |
|
|
P110 |
- |
0.6 |
758 |
862 |
862 |
- |
- |
|
|
4 |
Q125 |
All |
0.65 |
862 |
931 |
931 |
- |
- |
|
Standard |
Grade |
Composition(%) |
||||||||||
|
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S |
Cr |
Ni |
Cu |
Mo |
V |
AIs |
||
|
API SPEC 5CT |
J55K55 |
0.34~0.39 |
0.20~ |
1.25~1.50 |
≤0.020 |
≤0.015 |
≤0.15 |
≤0.20 |
≤0.20 |
|
|
≤0.020 |
|
(37Mn5) |
||||||||||||
|
N80 |
0.34~0.38 |
0.20~ |
1.45~1.70 |
≤0.020 |
≤0.015 |
≤0.15 |
|
|
|
0.11 |
≤0.020 |
|
|
(36 Mn2V) |
||||||||||||
|
L80(13Cr) |
0.15~0.22 |
≤1.00 |
0.25~1.00 |
≤0.020 |
≤0.010 |
12.0~ |
≤0.20 |
≤0.20 |
|
|
≤0.020 |
|
|
P110 |
0.26~0.35 |
0.17~ |
0.40~0.70 |
≤0.020 |
≤0.010 |
0.80~ |
≤0.20 |
≤0.20 |
0.15 |
≤0.08 |
≤0.020 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Ingot heating→Perforation→Rolling and sizing→Cooling→Straightening→NDT→End cutting→Coupling thread→Hydraulic test→Painting and thread protecting→Packing
Ingot heating

Ingot heating is a working procedure which make ingot meet the required temperature of the hot working process. The purpose of the ingot heating is to make the steel ingot have enough plasticity, reduce rolling deformation resistance, improve the internal organization.
Heating process of ingots mainly has two stages: heating stage (including low temperature and high temperature), the ingot surface temperature is increased to the tapping temperature; Uniform heating, to make ingot inside and outside temperature uniformity.
Rolling and sizing

Hot rolling can reduce energy consumption and cost significantly. The high metal plastic deformation and low deformation resistance, greatly reduce the energy consumption of hot rolled steel.
Hot rolling can improve the process performance of metal, eliminate casting defects and improve the processing performance of the alloy.
Hot rolled usually adopt large ingot casting, which not only improve the production efficiency, but also improve the rolling speed, to achieve continuous rolling process and create the conditions for automation.
Cooling

After the cooling, hot rolled steel tube is in a specific range. Compared to the traditional process of making the process, it can simplify the process, save energy, get the same or better mechanical properties.
NDT

Nondestructive Testing, shorted for NDT, is a widely-used method in pipeline inspection. It is a process of testing, inspecting and evaluating the quality and characteristics of the material without damaging the pipeline itself or affecting the later regular work of the pipe. In other words, after NDT testing, the part can still be put into practical use. NDT utilizes the changes in heat, sound and magnets caused by abnormal inner structure or flaws to inspect the internal and external defects of the material.
The common inspection methods of NDT are visual testing (VT), ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), hydrostatic testing.
Coupling thread

Threaded joints refers to the pipeline connecting piece with the screw thread, is a most common pipe in industry. Coupling thread makes connection of the pipe becomes more simple, replacement are also more easily and greatly saves the cost of the pipeline connection.
Threaded joints of industrial is generally made of metal and it can withstand high pressure. The material contents carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, brass, etc.
Hydraulic test

Hydrostatic test is an inspection method to reduce the risk of flaws in the pipe that might threaten its ability to withstand the maximum operating pressure. Hydrostatic testing inspects the integrity of pipelines by filling in the pipe with a non-compressible liquid (often water, dyed) to increase the pressure level above the normal pressure to see if there is any defect exists. It can either carried out on pipes prior to being put into service or on existing pipes that are already in service