Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Carbon steel pipe bending is an essential process in various industries, requiring both skill and precision. Knowing how to correctly bend carbon steel pipes can significantly impact project outcomes and efficiency. In this article, we'll explore the best techniques for carbon steel pipe bending, discuss the advantages and precautions, and help you make informed decisions.
Carbon steel pipes are known for their excellent mechanical properties, including ductility and tensile strength, making them ideal for bending applications. Here, we delve into the core principles and methods for achieving optimal bends without compromising the integrity of the pipe.
1. Prevent Wrinkling and Collapse: Bending causes compression inside the pipe, which can lead to wrinkling.
2. Prevent Ovality: Ovality affects fluid flow; maintaining a round cross-section is crucial.
3. Prevent Cracking: Excessive stretching can cause cracks, so ductility is important.
4. Compensate for Springback: Carbon steel tends to rebound slightly after bending, requiring overbending to correct this. Solution: Use appropriate tools and techniques tailored to pipe dimension and quality requirements.
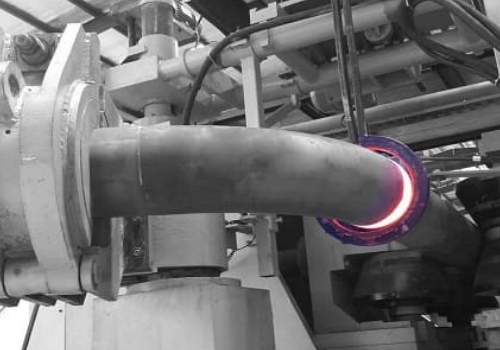
Hot bending involves heating the pipe to make it more pliable, ideal for larger diameters and thick walls.
· Temperature Control: Maintain 900-950°C for effective bending.
· Equipment: Medium-frequency induction heating ensures uniform heat distribution. Induction Heating
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low bending force, suitable for thick walls | Surface scale formation, requires post-treatment |
| Reduces cold work hardening | Complex operation, safety risks |
Cold bending is performed at room temperature and suits small diameter pipes.
· Manual Bending: Best for pipes DN15 and below, low-cost but labor-intensive.
· Roll Bending: Perfect for large radius bends, efficient but limited to non-small radius.

| Method | Tool | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Pipe bender | Low precision, may cause flattening |
| Roll | Three-wheel bender | No die needed, low efficiency |
| Press | Hydraulic bender | Quick, can deform cross-section |
| Circular | Bending die | High precision, costly |
1. Filling Method: Fill the pipe with dry sand to prevent collapse.
2. Heating Method: Heat till cherry red (700-950°C) for increased plasticity. Method Options for Simplicity:
· Spring Bender: Insert spring for support; suitable for small diameter pipes.
· Column Bending: Bend around a cylindrical guide.
· Press Bending: Apply pressure with supports; only for applications with minimal precision requirements.
1. Method Selection: Choose based on diameter, wall thickness, and required bend radius.
2. Speed Control: Stable bending speed is vital for quality.
3. Stress Reduction: Minimize stress concentration at bends.
4. Quality Inspection: Check for cracks or deformation after bending.
5. Corrosion Prevention: Reapply anti-rust coatings post-bending.
By understanding the intricacies of carbon steel pipe bending, you can efficiently meet project specifications and maintain pipe integrity. Whether opting for hot or cold methods, prioritizing quality control and careful technique application will result in successful and precise bends.