Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Square tube material refers to the metal composition and alloying process used to produce steel square tubing and other hollow structural sections (HSS). The quality, strength, and corrosion resistance of the finished tube depend directly on the selected square tube material, its chemical makeup, and how it is proportioned during melting and forming.
Square tubing is widely used in construction, automotive, machinery frames, agricultural tools, and furniture, where high rigidity and precise dimensions are required. To produce premium square tubes, manufacturers must follow strict mixing and alloying principles during production.
The performance of square tubing relies heavily on the composition of its base material. A precisely controlled square tube material ensures:
· High tensile and yield strength
· Good weldability and formability
· Uniform wall thickness and shape stability
· Enhanced corrosion resistance and long service life
If the alloy proportions or raw material quality deviate, issues such as brittleness, weak weld joints, or deformation during forming may occur.
Understanding different types of square tube material helps engineers and buyers choose the right option for each application:
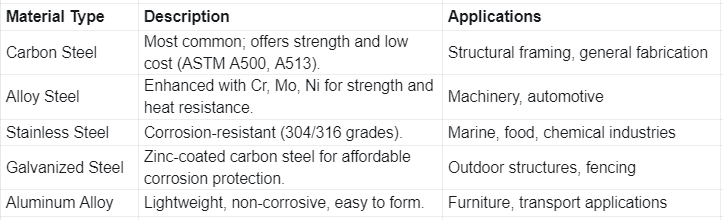
Each square tube material type should be selected according to environment, load requirement, and budget.
High-quality square tube production depends on strict adherence to proportioning principles. These include:
Theoretical calculations of alloy additions (like carbon, manganese, silicon, chromium) must be combined with practical melting experience. Real-world furnace losses and reduction rates can vary, so the formula must be adjusted accordingly.
Producers must understand how elements behave during the melting process—some burn off (oxidize), while others are reduced. This helps ensure accurate adjustment when determining the final square tube material composition.
All alloying elements should ideally be added once to stabilize chemical balance in the furnace. Repeated additions can cause unpredictable fluctuations in material properties.
Every metal input—whether virgin iron, scrap steel, or ferroalloys—must be precisely weighed and recorded. Only accurate batching guarantees consistent square tube material quality.
During smelting, certain elements will reduce or burn off; these must be subtracted or compensated to reach the target alloy composition accurately.
The square tube material undergoes several critical stages from raw input to finished product:
1. Raw Material Preparation – Inspect billets or coils for correct chemistry and cleanliness.
2. Melting & Alloying – Smelt in induction or electric arc furnaces, adjusting elements as needed.
3. Forming & Welding – Roll steel into circular sections, weld the seam, then form into square shapes.
4. Sizing & Straightening – Use precision rollers to maintain consistent dimensions.
5. Heat Treatment – Normalize or anneal for improved mechanical performance.
6. Surface Finishing – Galvanizing, painting, or polishing to meet corrosion and aesthetic requirements.
7. Inspection & Testing – Perform ultrasonic testing, tensile strength analysis, and dimensional verification.
Every step ensures that the square tube material meets international standards such as ASTM A500 or EN 10210.
When selecting the right square tube material for your project, consider the following:
· Structural Load Requirements: Heavier loads need high-strength carbon or alloy steel.
· Environmental Conditions: Use galvanized or stainless steel for humid, marine, or chemical environments.
· Fabrication Needs: Choose materials with good weldability and machinability.
· Budget: Carbon steel offers great cost-to-strength ratio; stainless provides longevity at a higher cost.
· Compliance: Always request mill test certificates (MTC) and ensure compliance with ASTM or ISO standards.
To ensure top-grade square tubing:
· Use non-destructive testing (NDT) for internal defects.
· Verify mechanical properties—tensile, yield, elongation.
· Check dimensional accuracy and corner squareness.
· Conduct corrosion and coating adherence tests for galvanized products.
Only after passing all inspections is the square tube material approved for shipment.
Q1: What is the best material for square tubing?
For structural applications, carbon steel (ASTM A500 Grade B/C) is the most common and economical square tube material. For corrosion resistance, stainless or galvanized steel is preferred.
Q2: Can aluminum square tubing replace steel?
Yes, for lightweight applications such as frames or furniture, aluminum square tubes work well, though they have lower strength.
Q3: How is the chemical composition of square tube material controlled?
Producers use spectrometers and strict batching methods to monitor alloy elements like carbon, manganese, and chromium, ensuring stable composition and consistent performance.
Q4: What standards define square tube material quality?
Common standards include ASTM A500, A513, EN 10210, and GB/T 6728, specifying mechanical and chemical requirements for different grades.
The square tube material you choose determines not only the strength and performance of your structure but also long-term durability and cost efficiency. By understanding alloying principles, selecting the right grade, and ensuring proper manufacturing control, you can achieve exceptional results in any engineering or fabrication project.
Whether you’re sourcing carbon steel tubing for industrial framing or stainless square tubes for outdoor structures, following these principles ensures your square tube material delivers maximum performance and reliability.