Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Sharing China-Made with Global Customers

Corrosion destroys pipeline projects and drains your budget rapidly. You cannot afford constant repairs or unexpected leaks in your construction work. Fusion bonded epoxy coated carbon steel pipe uses a thermosetting powder coating to create a hard, chemical-resistant barrier. It protects steel against severe corrosion, soil stress, and moisture, ensuring your pipeline system lasts for decades without frequent maintenance.
I see many managers struggle with choosing the right protection for their projects. I want to explain why this specific coating is the industry standard today and how it saves money for my clients at Centerway Steel.
Improper application leads to peeling and failure. You need to know if the factory follows the right steps to ensure longevity. The process involves heating the pipe to over 200°C and spraying electrically charged epoxy powder. This powder melts and cures onto the steel surface, forming a permanent, irreversible bond that resists physical damage and heat.

At Centerway Steel, we treat the application process as the most critical step. We do not just paint the pipe. We chemically fuse the protection to the steel. The process starts with surface preparation. We blast clean the steel to a "near-white" metal finish. This removes all rust, mill scale, and grease. The steel must be rough enough for the coating to grip tight. Next, we heat the pipe using induction heating. The temperature reaches between 230°C to 250°C. We spray the epoxy powder immediately. The powder hits the hot steel and melts. It turns into a liquid gel. Then, it quickly cures into a solid. This is a chemical reaction. It creates cross-linked chains in the material. The coating becomes a hard, plastic-like shield. It will not melt again, even if you heat it. We test every batch. We check for thickness and holidays (pinholes). This ensures the fusion bonded epoxy coated carbon steel pipe can withstand rough handling during transport and installation.
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Surface Prep | Abrasive blast cleaning | Removes contaminants and creates an anchor profile. |
| 2. Heating | Induction heating (230°C+) | Prepares the steel for chemical bonding. |
| 3. Powder Spray | Electrostatic application | Ensures uniform coverage of the epoxy powder. |
| 4. Curing | Heat maintenance | Allows the powder to cross-link and harden. |
| 5. Quenching | Water spray cooling | Stops the reaction and hardens the coating for handling. |
Using the wrong pipe in salty soil or chemical environments is a disaster. You risk project shutdown if the pipes fail early. You need this coating for underground burial, underwater pipelines, or transport of corrosive fluids. It effectively blocks oxygen and moisture from reaching the steel, preventing rust even in high-temperature or high-pressure environments.

You must consider the environment surrounding your project. I have supplied pipes for projects in the Middle East and Southeast Asia. The soil there is often salty or wet. Bare steel rusts in months. Fusion bonded epoxy coated carbon steel pipe is the standard solution here. It provides an excellent barrier against soil chemicals. It also resists bacteria in the soil that eat metal. Another major use is for pipelines with Cathodic Protection (CP). FBE is compatible with CP systems. It acts as an electrical insulator. It does not shield the CP current. If the coating gets a scratch, the CP system protects the exposed metal. Other coatings might block this protection. We also see high demand for FBE in water transport. It creates a smooth surface inside the pipe. This reduces friction. You can pump fluids faster with less energy. It also prevents dangerous buildup inside the pipe. This is vital for drinking water or sewage lines.
| Environment | Threat Level | Why FBE Works |
|---|---|---|
| Underground (Buried) | High | Resists soil stress and chemical attack from groundwater. |
| Underwater (Subsea) | Extreme | Compatible with concrete weight coatings and cathodic protection. |
| High Temperature | Medium/High | Retains integrity up to 110°C (standard) or higher (specialized). |
| Potable Water | Low/Medium | Non-toxic, improves flow, prevents internal rust contamination. |
Choosing the most expensive option is not always right. You might waste budget on 3LPE when FBE is sufficient. While 3LPE offers extra physical protection, FBE provides superior adhesion to the steel surface and resists cathodic disbondment better. It is often more cost-effective for standard high-corrosion environments compared to multi-layer systems.
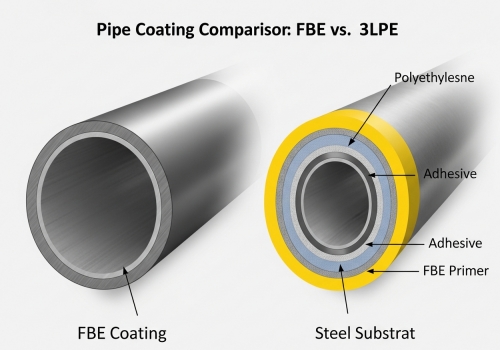
I get asked this question often by EPC managers. Should they buy 3-Layer Polyethylene (3LPE) or FBE? 3LPE has an FBE layer, an adhesive, and a plastic outer layer. It is thicker. It is tough against rocks. But it costs more. For many projects, fusion bonded epoxy coated carbon steel pipe is the smarter buy. FBE has one huge advantage: adhesion. It sticks to the steel better than anything else. If water penetrates a 3LPE coating, it can travel under the plastic layer. This hides corrosion. With FBE, the damage stays at the scratch. It does not spread under the coating. This makes inspection easier. Also, consider the operating temperature. Standard polyethylene softens at around 80°C. FBE stays hard and stable at higher temperatures. If your pipeline transports hot oil or gas, FBE is often safer. Finally, think about field joints. When you weld pipes together, you must coat the weld area. FBE is easy to apply in the field. 3LPE field joints are complex and expensive. FBE saves you time and money during the construction phase.
| Feature | FBE Coating | 3LPE Coating | Galvanized |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Moderate | High | Low/Moderate |
| Adhesion to Steel | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Excellent | Moderate |
| Max Temp | ~110°C | ~80°C | ~200°C |
| Field Repair | Easy | Difficult | Easy |
Fusion bonded epoxy coated carbon steel pipe offers the best balance of cost, corrosion resistance, and longevity for underground and industrial projects, ensuring your pipelines remain safe and operational.